
Imagine you could tell how long your excavator will remain idle during a project so that you can utilize it somewhere else. Or how you can ideally allocate your expensive crane to the rigging crew, given the small lay down yard you have in a structural steel construction job? The amount of savings is not negligible particularly when project grows in size.
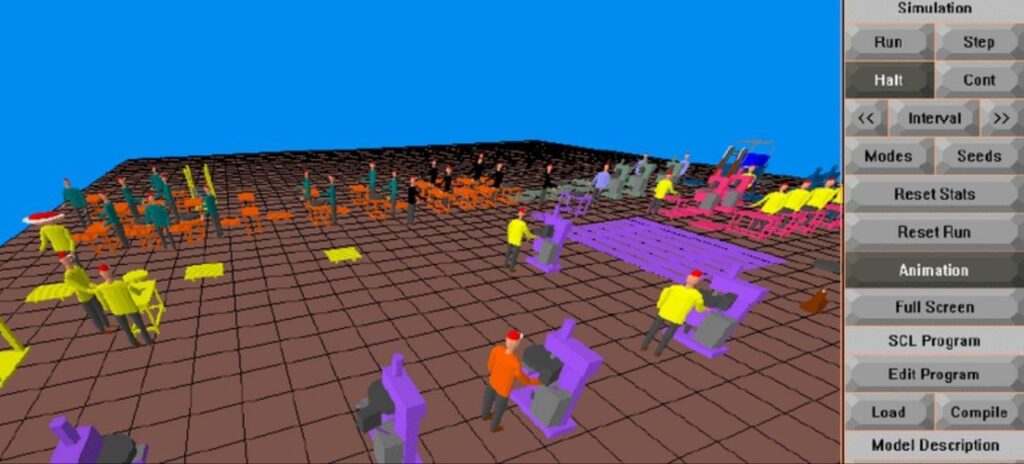

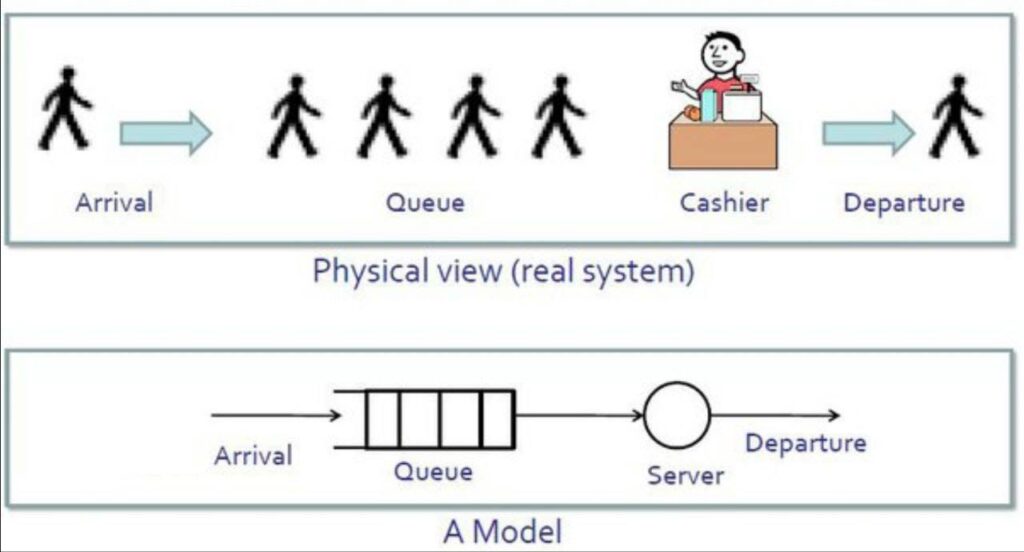
At PPME, we use state-of-the-art discrete event simulation to model construction processes before the projects begin to assess constructability of the project, to determine resource utilization, and to save time, and cost during feasibility phase. Discrete Event Simulation (DES) is a powerful technique used in construction project management to model and analyze complex systems and processes. Here are the key benefits of employing discrete event simulation in construction project management:
Visualization of Project Processes:
DES allows project managers to visually represent the entire construction process in a dynamic and interactive model. This visualization helps in understanding the flow of activities, resource interactions, and dependencies within the project.
Identification of Bottlenecks and Critical Paths:
By simulating the construction activities, DES can identify potential bottlenecks and critical paths that could impact project schedules. This insight enables managers to optimize resource allocation and sequencing to minimize delays and improve project efficiency.
Assessment of Schedule Reliability:
DES provides a platform to assess the reliability of project schedules by considering uncertainties and variability in task durations, resource availability, and external factors. It helps in evaluating different scheduling scenarios and predicting the likelihood of meeting project deadlines.
Resource Optimization and Utilization:
Through simulation, construction managers can analyze resource utilization patterns and identify opportunities for optimization. This includes determining the optimal number of workers, equipment usage, and material handling strategies to maximize productivity while minimizing costs.
Risk Analysis and Mitigation:
DES enables proactive risk analysis by simulating various risk scenarios such as material shortages, equipment breakdowns, or weather disruptions. By quantifying the impact of risks on project performance, managers can develop effective mitigation strategies to enhance project resilience.
Decision Support for Project Planning:
Simulation models can be used as decision support tools for project planning and management. Managers can evaluate alternative scenarios, assess the impact of changes or constraints, and make informed decisions to optimize project outcomes.
Improved Communication and Stakeholder Engagement:
DES facilitates better communication among project stakeholders by presenting complex information in a visual and understandable format. It helps in fostering collaboration, aligning expectations, and gaining consensus on project strategies.
Continuous Improvement and Lessons Learned:
By simulating construction processes and analyzing performance metrics, DES supports continuous improvement initiatives. Managers can capture lessons learned from simulations to refine project plans, enhance workflows, and implement best practices in future projects.
